Housing Diversity
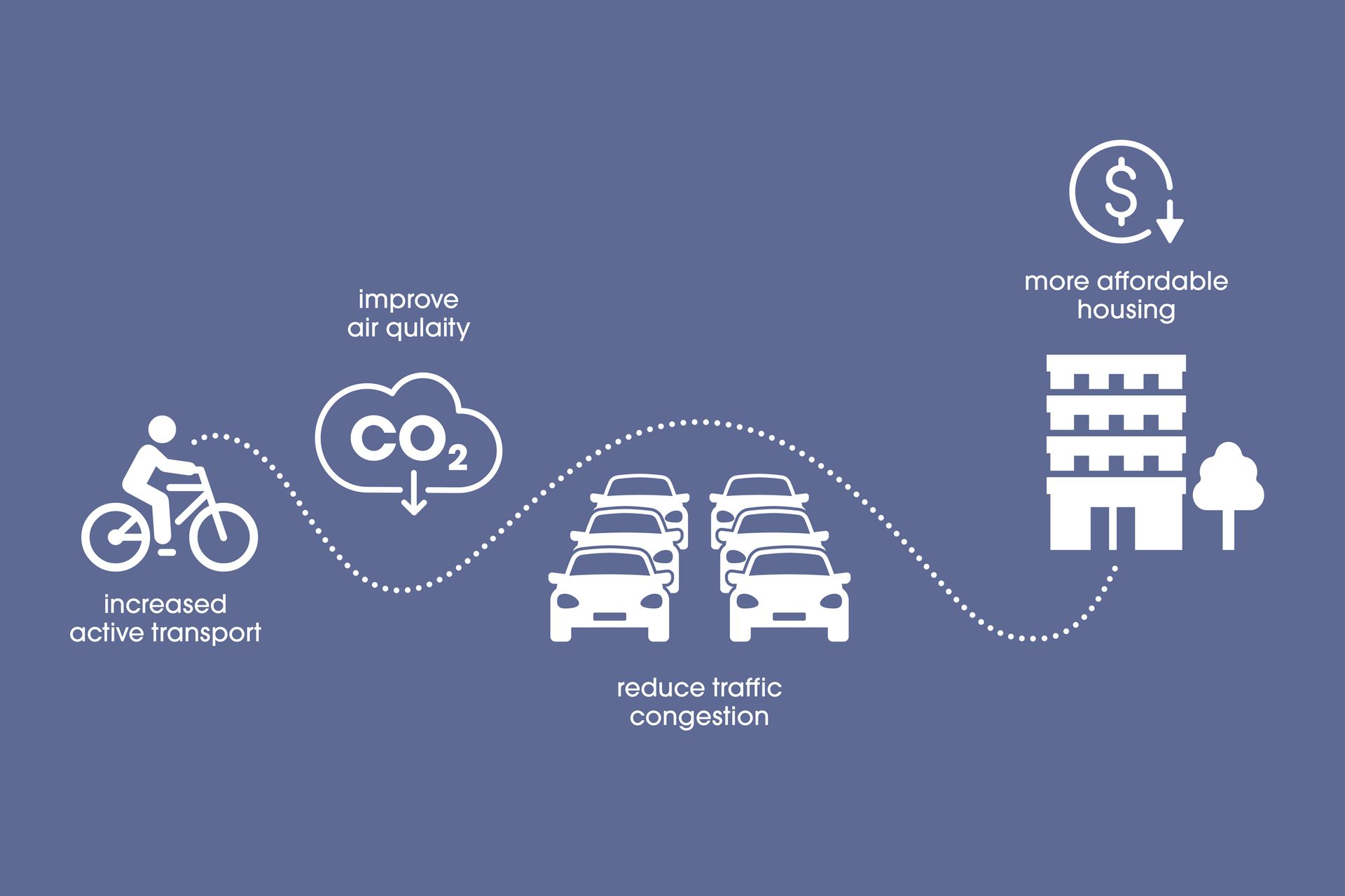
A mix of housing types and lot sizes increases residential density which, in turn, helps create a local population large enough to support a vibrant community. Higher density and a mix of housing produces a more diverse range of residents and this increased population, density and vibrancy tends to mean a broader range of services can be supported within walking or cycling distance. Housing diversity also supports older residents by providing suitable and affordable housing options as they age – all within walking distance of destinations they are already familiar with. This section includes many examples of innovative housing diversity, including urban renewal projects and planned communities.
Features and benefits of housing diversity:
- Higher residential density close to local, neighbourhood and district centres supports the local economy.
- Public transport linking areas of higher residential density forms a network of conveniently accessible destinations.
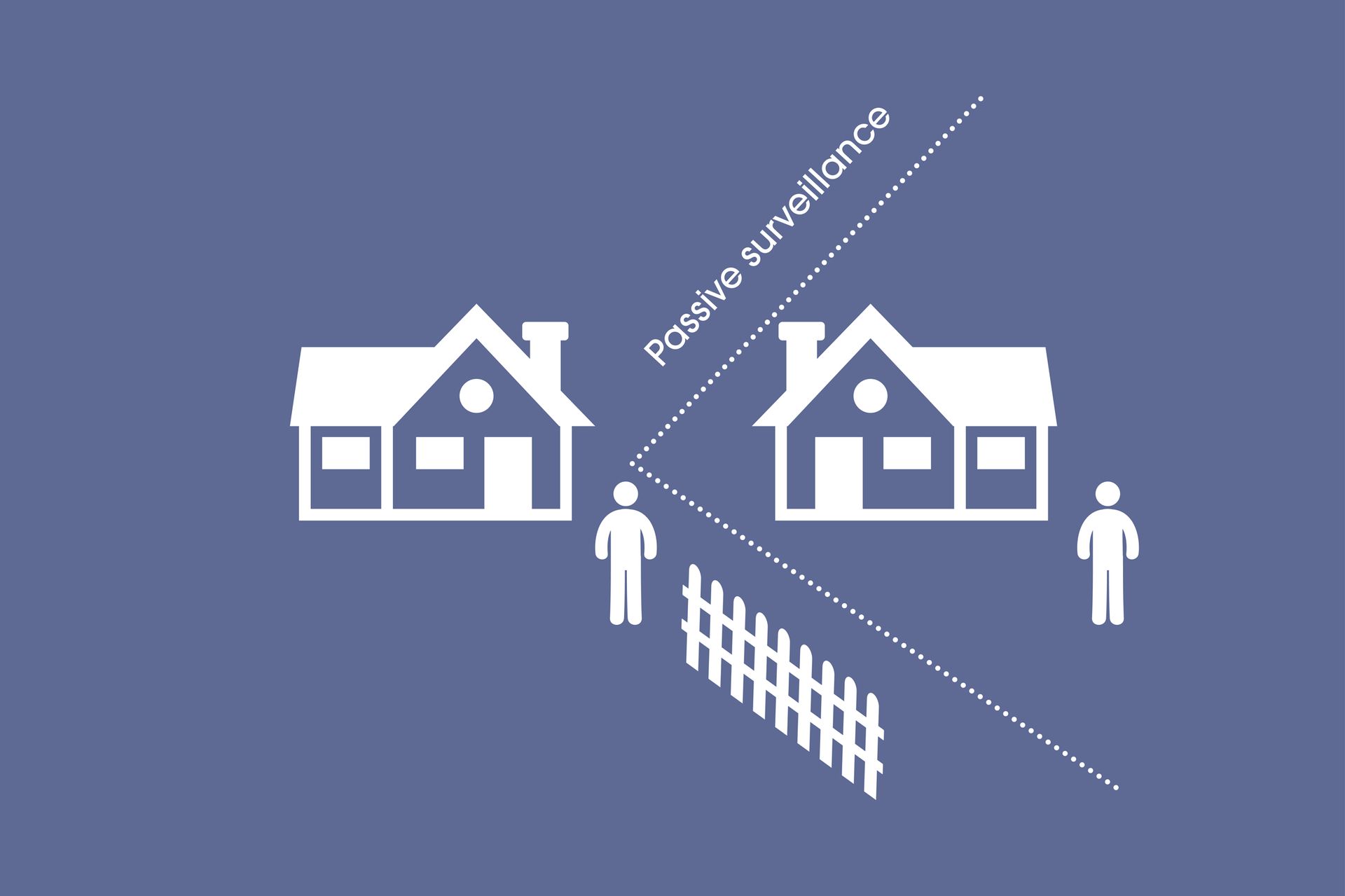
- Higher residential density near parks and other public open spaces encourages passive surveillance.
- Student housing located within walking distance of a university campus reduces traffic congestion.
- Aged-care accommodation co-located with mixed-use centres gives older residents easier access to services.
Authors: Alex Kleeman, Dr Lucy Gunn, Professor Billie Giles-Corti.
Detailed further guidance on this design feature is available on our
Publications and Policies page.
Each additional kilometre walked per day in mixed use environments was associated with a 4.8% reduction in the likelihood of obesity. An increase in land use mix is associated with a 12.2% reduction in the likelihood of obesity
What do we mean by ‘housing diversity’?
The term housing diversity refers to the range of housing types in a development or neighbourhood. A diverse neighbourhood has various different dwelling types and sizes – usually achieved by offering a wider range of lot sizes and promoting a variety of building forms. By providing greater housing choice, developments can meet the housing needs of increasingly diverse residents and household types (such as young families, professionals, retirees, people with disabilities) across the life course.
Conversely, a wider choice of housing and lifestyles attracts a more diverse range of people to a location. Smaller lots and the mixing of compatible uses within and around town centres and near public transport creates the higher densities needed to support destinations and services that residents can easily reach by walking or cycling.
Residential density, at its simplest, is a measure of the number of residents or dwellings in a given area. But there is no universally agreed definition of residential density, and different professions have applied and defined the concept in various ways.
Two major points of difference and confusion are the base land-area calculation (the denominator) and the inclusion and exclusion of different types of land. [1] In the literature on physical activity, residential density has typically been defined as the number of people living in a given area (population per hectare) or the number of housing units in an area (residences per hectare).
Increased density, when carefully planned, can produce numerous benefits to the environment and health of the community
Many types of dwelling can combine to achieve housing diversity:
- Single dwellings and detached houses, whether single-storey or multiple-storey. The majority of Australia’s suburbs are made up of single dwellings. An ancillary dwelling can be added to a single lot – usually behind the main dwelling – so that elderly relatives can more easily be cared for by younger family members.
- Survey strata lots are a single lot that has been divided into multiple separate smaller lots. They usually contain a smaller single house – known as duplex or triplex units – or grouped dwellings. Traditionally, this is the second-most common form of housing in Australia.
- Town houses are single or multiple dwellings of two or more storeys. They are mostly found in the inner suburbs.
- Multiple dwellings or apartments are strata-title developments where multiple landowners occupy separate dwellings within the one complex. These are more likely to be found near high-frequency transport, or in transit-oriented developments.
- Mixed-use development combines residences with commercial or retail activities. The dwellings tend to be multiple-unit developments, with commercial operations located on the ground floor.
- Specialised housing comes in various types, including single-bedroom dwellings, retirement villages, dwellings for people over 55 years and their carers, aged-care facilities, and holiday accommodation.
Streets with dwellings designed to have increased opportunities for passive surveillance, are 60% less likely to have incidence of graffiti, litter, vandalism and broken windows
Download the Housing Diversity infographic
Stay informed. Sign up to our newsletter.
I agree that I have read and I accept the Heart Foundation's Privacy Statement.